As the world shifts towards sustainable solutions, the food industry is increasingly adopting compostable takeout containers to minimize environmental impact. These containers offer an eco-friendly alternative to conventional packaging, providing a way to serve food without contributing to plastic waste. In this article, we'll explore the essential materials used in eco-friendly takeout containers, the decomposition process, benefits for restaurants, how to verify their compostability, and real-world applications. Whether you're a restaurant owner, a consumer, or an environmental enthusiast, understanding these concepts will help you make informed decisions about sustainable dining practices.

Key Materials in Compostable Packaging
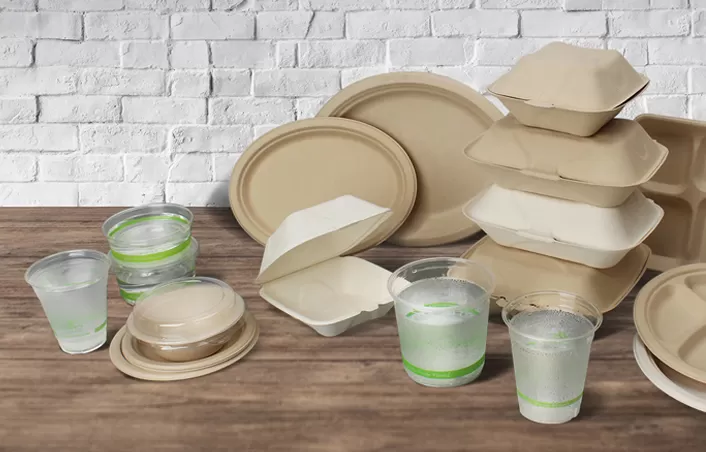
Compostable packaging is crafted from materials that can break down into natural elements when subjected to composting conditions. The most commonly used eco friendly food containers are made from renewable resources. Here's a closer look at these materials:
Material | Description | Properties |
PLA (Polylactic Acid) | Bioplastic derived from cornstarch, sugarcane, or tapioca roots. | Compostable, biodegradable, heat-resistant |
Bagasse | Fiber sourced from the residue left after extracting juice from sugarcane. | Sturdy, water-resistant, compostable |
Other plant-based fibers | Fibers extracted from plants like wheat straw and palm leaves. | Durable, biodegradable, lightweight |
Pulp paper | Recycled paper turned into sturdy, moldable material. | Recyclable, compostable, customizable |
Utilizing these materials in disposable food packaging ensures that the products not only serve their intended purpose but also degrade without leaving harmful residues.
Decomposition Process Explained
To fully appreciate compostable takeout containers, understanding the decomposition process is essential. When disposed of properly, these containers degrade in industrial composting facilities or at-home compost settings.
The decomposition process involves several stages:

Fragmentation: Initial breakdown into smaller pieces via microbial activity or mechanical forces.
Microbial Digestion: Microorganisms feed on the organic matter, further breaking it down into simpler compounds.
Mineralization: Conversion of organic matter into minerals and water.
Final Integration: Residual materials assimilated into the soil, enriching it with nutrients.
This cycle typically occurs within 90-180 days, depending on environmental conditions and the material composition. Through this process, compostable cold cups and other takeout containers support a closed-loop system that reduces waste and enhances soil quality.
Benefits for Restaurants
Restaurants adopting compostable takeout containers gain multiple advantages, aligning their business practices with eco-conscious consumer demands. Key benefits include:
Enhanced Brand Image: Demonstrating a commitment to sustainability strengthens reputation and attracts eco-minded customers.
Reduced Waste: Compostable containers lower landfill contributions and decrease plastic pollution.
Compliance with Regulations: Adhering to local, national, and international standards on packaging materials averts potential fines and alignments with green policies.
Cost Effectiveness: Though initial costs might be higher, long-term savings in waste management can offset expenses.
Customer Satisfaction: Consumers increasingly prefer establishments that support sustainable practices, boosting customer loyalty.
For restaurants, utilizing disposable biodegradable food containers is more than an ecological choice—it's a strategic business decision that caters to the evolving expectations of their clientele.
How to Verify Compostability
To confirm the compostability of packaging, restaurants and consumers should look for certain labels and certifications. These indicators ensure the containers meet composting standards:
BPI Certification: The Biodegradable Products Institute issues this certification for products meeting ASTM D6400 or D6868 standards.
Compost Manufacturing Alliance (CMA): Provides testing and verification for compostable products.
EN 13432: European standard verifying biodegradability and compostability.
Product Labelling: Look for terms such as "compostable," "biodegradable," alongside the associated logos.
By selecting eco friendly containers with these formal verifications, stakeholders can ensure their products are genuinely compostable, contributing to waste reduction and environmental preservation.
Real-World Applications
The adoption of disposable steam table pans and compostable takeout containers spans various sectors, proving their versatility and sustainability. Here are some practical applications:
Food Services:Facilitating eco-friendly options for takeout and delivery in restaurants.
Events and Catering: Providing sustainable solutions for large-scale events where disposable containers are necessary.
Retail and Grocery Stores: Offering sustainable packaging options for deli, salad bars, and ready-to-eat meals.
Corporate Spaces: Implementing environmentally conscious dining applications in office cafeterias and kitchens.
These applications illustrate how entities across different domains can embrace compostable paper containers for food to promote environmental responsibility while meeting operational needs.
Conclusion
The transition to compostable takeout containers represents a significant development in reducing our environmental footprint. Understanding the materials involved, their decomposition process, and the benefits for businesses reinforces the importance of embracing sustainable practices. As consumers demand greener solutions and regulations tighten, compostable containers provide a viable, responsible alternative to conventional materials. By making informed choices, restaurants and individuals contribute positively to environmental preservation and demonstrate a commitment to sustainability. Adopting these containers not only supports ecological goals but also aligns businesses with the evolving expectations of today's eco-conscious clientele.
References:
ASTM D6400 Standard
Biodegradable Products Institute (BPI)
Compost Manufacturing Alliance (CMA)
European EN 13432 Standard